Institute కి రండి | Demo వినండి | Decide అవ్వండి. ( Online Class Available )
WordPress Tutorial for beginners - Step by Step Guide 2026
WordPress Tutorial for beginners
Introduction to WordPress
Overview of WordPress
WordPress is the most popular Content Management System (CMS) that allows users to create and manage websites with ease. Launched in 2003, it started as a simple blogging platform but has since evolved into a powerful website-building tool used by individuals, businesses, and organizations globally.
With over 40% of all websites on the internet powered by WordPress, it is known for its flexibility, user-friendly interface, and vast customization options. Whether you want to build a personal blog, an online store, a portfolio, or a corporate website, WordPress provides the tools needed to bring your vision to life.
Why Choose WordPress for Website Creation?
There are several reasons why WordPress is the preferred choice for website creation:
- Free and Open-Source – WordPress is free to use, modify, and distribute. The open-source nature allows developers to contribute and improve the platform continuously.
- User-Friendly – WordPress does not require coding knowledge. With its simple interface and drag-and-drop features, even beginners can create professional websites without technical expertise.
- Highly Customizable – Thousands of themes and plugins allow users to design unique websites with advanced functionality, from SEO optimization to eCommerce integration.
- SEO-Friendly – WordPress is built with clean code and provides SEO-friendly features, making it easier for websites to rank higher on search engines like Google.
- Scalability – Whether you’re starting a small blog or managing a high-traffic business website, WordPress can scale to meet your needs without compromising performance.
- Large Community Support – Millions of developers, designers, and users contribute to the WordPress ecosystem, providing extensive documentation, forums, and tutorials for troubleshooting and learning.
- Secure and Reliable – With regular updates and security plugins, WordPress ensures that websites remain secure from vulnerabilities and cyber threats.
Difference Between WordPress.com and WordPress.org
Feature | WordPress.com | WordPress.org |
Hosting | Hosted by WordPress | Self-hosted (requires third-party hosting) |
Customization | Limited themes and plugins | Full access to themes, plugins, and code customization |
Cost | Free with limitations (Paid plans available) | Free, but requires hosting and domain purchase |
Monetization | Limited ad revenue options | Full control over monetization (Ads, eCommerce, Memberships) |
Control | Restricted by platform rules | Complete control over website and data |
Which One Should You Choose?
WordPress.com is suitable for hobby bloggers and users who want a simple, managed solution without worrying about technical aspects.
WordPress.org is the best option for those who need full control over their website, customization, and monetization opportunities.
Who Should Use WordPress?
- Bloggers & Writers – Create and manage blogs with engaging content, images, and multimedia elements.
- Business Owners – Build professional websites to showcase products, services, and company information.
- eCommerce Entrepreneurs – Sell products online using WooCommerce, a powerful eCommerce plugin.
- Freelancers & Creatives – Showcase portfolios, photography, and artwork with visually stunning themes.
- Developers & Designers – Customize websites, develop themes, and extend WordPress functionalities with coding.
- Non-Profit Organizations – Create donation portals, event pages, and awareness campaigns.
- Educational Institutions – Build e-learning platforms, online courses, and student portals.
Watch the video to know about WordPress:
What is a Content Management System?
A CMS (Content Management System) is a software application that allows users to create, manage, and modify content on a website without needing specialized technical knowledge. It provides an intuitive interface for handling digital content, making website development and maintenance accessible to users with little or no coding experience.
How a CMS Works
A CMS consists of two main components:
Content Management Application (CMA): The user-facing part of the system that allows non-technical users to create, edit, and manage content through a graphical interface.
Examples: Text editors, drag-and-drop page builders, and media upload tools.
Content Delivery Application (CDA): The backend system that processes and delivers the content to the website visitors.
Manages databases, stores content, and ensures that updates are reflected on the live site.
Click the link below to know more about CMS:
System Requirements for WordPress installation
- If you are using Windows, you need to install WAMP (Windows, Apache, MySQL, and PHP).
- If you are using Linux, you need to install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP).
- If you are using a Mac, you need to install MAMP (Macintosh, Apache, MySQL, and PHP).
- Alternatively, you can install XAMPP, a cross-platform solution that includes Apache, MariaDB, PHP, and Perl.
- WordPress is compatible with PHP 5.2+ and MySQL 5.0+.
Setting Up WordPress
Creating a WordPress website begins with setting up the right foundation. This includes choosing a domain name, selecting a reliable hosting provider, installing WordPress, and logging into the WordPress dashboard.
What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is your website’s unique address on the internet (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com). It helps users find and access your site easily.
Tips for Choosing a Good Domain Name:
- Keep it Short and Simple – A short, memorable domain name is easier to type and recall.
- Use Keywords – If possible, include relevant keywords that describe your business or niche (e.g., besttravelguides.com).
- Avoid Numbers and Hyphens – These can make a domain name confusing and harder to remember.
- Choose the Right Extension – .com is the most common and trusted, but you can also consider .org, .net, or industry-specific extensions like .tech or .store.
- Check Availability – Use domain registrars like Namecheap, GoDaddy, or Google Domains to see if your desired name is available.
Best WordPress Hosting Providers:
- Bluehost – Recommended by WordPress, affordable plans, free domain for one year.
- SiteGround – Excellent customer support, fast performance, and high security.
- Hostinger – Budget-friendly, great for beginners, and easy WordPress installation.
- WP Engine – Best for managed WordPress hosting, high performance, and security.
- DreamHost – Officially recommended by WordPress, easy-to-use interface, and free SSL.
Installing WordPress via cPanel or One-Click Install
Once you have chosen your domain and hosting, the next step is to install WordPress.
Method 1: Installing WordPress via One-Click Install
Most hosting providers offer a one-click WordPress installation to make the setup process easy.
Steps to Install WordPress with One-Click Installer:
- Log in to your hosting account.
- Go to the control panel (cPanel) or dashboard.
- Find the WordPress Installer (Softaculous, QuickInstall, or Fantastico).
- Click Install WordPress and select your domain.
- Fill in your website details:
- Site Name (Example: My Blog)
- Admin Username & Password (for WordPress login)
- Admin Email (for password recovery)
- Click Install and wait for the process to complete.
- Once installed, you will see a confirmation message with your WordPress login URL.
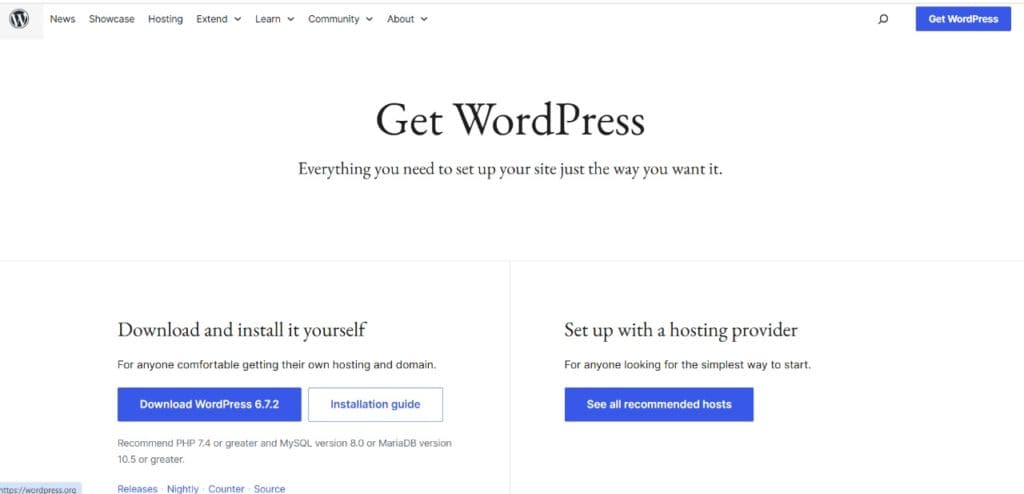
Method 2: Installing WordPress Manually via cPanel
For users who prefer manual installation, follow these steps:
- Download WordPress from the official website (wordpress.org).
- Log into cPanel and open the File Manager.
- Upload the WordPress ZIP file to the public_html folder and extract it.
- Create a MySQL Database:
- Open MySQL Databases in cPanel.
- Create a new database and user, then assign full permissions.
- Configure WordPress:
- Open yourwebsite.com/wp-admin/setup-config.php.
- Enter the database name, username, and password.
- Click Submit and follow the setup instructions.
- Complete Installation by entering your site title, admin credentials, and clicking Install WordPress
Watch the video for wordpress Installation:
Logging into the WordPress Dashboard
Once WordPress is installed, you need to log into the admin dashboard to start customizing your website.
How to Log into WordPress?
- Open a web browser and go to:
- yourwebsite.com/wp-admin
- Enter your admin username and password (created during installation).
- Click Log In, and you will be redirected to the WordPress dashboard.
Understanding the WordPress Dashboard
Once you have installed WordPress, the next step is to familiarize yourself with the WordPress Dashboard—the central hub where you manage and control your website. This section will cover the overview of the admin panel, key settings configurations, and how to customize your site for better performance and user experience.
1. Overview of the WordPress Admin Panel
What is the WordPress Dashboard?
The WordPress Dashboard (also known as the Admin Panel) is the control center of your website. It allows you to manage content, customize the appearance, install plugins, configure settings, and much more.
How to Access the WordPress Dashboard
- Open your browser and go to: yourwebsite.com/wp-admin
- Enter your Admin Username and Password (created during installation).
- Click Log In, and you will be redirected to the Dashboard.
Main Components of the WordPress Dashboard
When you log in, the dashboard consists of multiple sections:
- Admin Toolbar (Top Bar): Quick access to website preview, updates, and user profile settings.
- Sidebar Menu (Left Panel): Contains all WordPress management options, including Posts, Pages, Media, Plugins, Users, and Settings.
- Main Dashboard Area: Displays site activity, quick shortcuts, and WordPress news.
- Screen Options & Help: Customize the appearance of the dashboard and access WordPress documentation.
Important Sections in the WordPress Dashboard
Section | Purpose |
Dashboard Home | Provides an overview of your site’s activity and updates. |
Posts | Create and manage blog posts. |
Pages | Add static pages like About Us and Contact. |
Media | Manage images, videos, and other media files. |
Comments | Moderate and respond to comments from visitors. |
Appearance | Customize themes, menus, widgets, and site layout. |
Plugins | Install and manage plugins to add extra features. |
Users | Add and manage user roles and permissions. |
Settings | Configure essential website settings. |
2. General Settings Configuration
The General Settings section allows you to set up basic information about your site.
How to Access General Settings?
- Log into your WordPress Dashboard.
- Go to Settings > General from the sidebar.
Key Settings to Configure:
- Site Title & Tagline:
Example: Site Title: “Tech World”
Tagline: “Latest Tech News & Updates”
- WordPress Address (URL) & Site Address (URL):
If your site is on https://www.yourwebsite.com, ensure both URLs match.
- Administration Email Address:
Enter a valid email to receive site notifications.
- Membership:
Enable or disable user registrations.
- Timezone, Date, and Time Format:
Set the correct timezone for scheduled posts.
Why Are General Settings Important?
- Ensure your website is properly configured from the start.
- Helps in branding by setting the right site title and tagline.
- Keeps you updated with email notifications for security and updates.
3. Writing & Reading Settings
Writing Settings
The Writing Settings section helps define how new content is created and published.
How to Access Writing Settings?
Go to Settings > Writing in the dashboard.
Key Options:
- Default Post Category: Choose the default category for new blog posts (e.g., News, Tutorials).
- Default Post Format: Select the format (e.g., Standard, Video, Image).
- Update Services: Automatically notify search engines when new content is published.
Reading Settings
The Reading Settings section determines how content is displayed on your website.
How to Access Reading Settings?
Go to Settings > Reading in the dashboard.
Key Options:
- Homepage Display: Choose between a static homepage or your latest blog posts as the main page.
- Blog Page Show At Most: Set the number of posts per page (default: 10).
- Syndication Feeds Show The Most Recent: Controls the number of articles displayed in RSS feeds.
- Search Engine Visibility: Enable or disable search engine indexing (keep it disabled for SEO).
Why Writing & Reading Settings Are Important?
- Helps customize how your website content is displayed.
- Ensures the homepage and blog layout meet your requirements.
- Controls how search engines index your content.
4. Discussion & Permalink Settings
Discussion Settings (Managing Comments)
The Discussion Settings section controls how comments and interactions work on your site.
How to Access Discussion Settings?
Go to Settings > Discussion in the dashboard.
Key Options:
- Allow or Disable Comments: Enable/disable comments for posts and pages.
- Comment Moderation: Approve or delete comments before publishing.
- Email Notifications: Get alerts when a comment is posted.
- Avatar Settings: Customize how user avatars appear in comments.
Why Discussion Settings Are Important?
- Helps prevent spam and abusive comments.
- Keeps discussions active and engaging.
- Allows full control over user interactions.
Permalink Settings (URL Structure)
The Permalink Settings section helps define how your URLs look in browsers.
How to Access Permalink Settings?
Go to Settings > Permalinks in the dashboard.
Key Options:
- Plain: yourwebsite.com/?p=123 (Not SEO-friendly)
- Day and Name: yourwebsite.com/2026/02/12/sample-post/
- Month and Name: yourwebsite.com/2026/02/sample-post/
- Post Name (Recommended for SEO): yourwebsite.com/sample-post/
- Custom Structure: /category/post-name/
Why Permalink Settings Are Important?
- Helps improve SEO rankings with clean, readable URLs.
- Makes URLs more user-friendly and shareable.
- Helps search engines index your content better.
Here is the short Video for understanding wordpress dashboard :
Choosing and Installing a WordPress Theme
A WordPress theme determines the design, layout, and overall appearance of your website. Choosing the right theme is essential for creating a visually appealing and functional website. In this section, we will explore the differences between free and premium themes, how to choose the right theme, and the step-by-step process of installing a theme from the WordPress repository or uploading a custom theme.
1. Free vs. Premium Themes
WordPress offers thousands of free and premium themes, each catering to different needs. Before selecting a theme, it’s essential to understand the pros and cons of both options.
Free Themes
These themes are available in the WordPress Theme Directory and can be installed directly from the dashboard.
Advantages:
- Completely Free: No cost involved.
- Easy to Install: One-click installation from the WordPress dashboard.
- Officially Reviewed: WordPress ensures these themes meet basic security and performance standards.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Features: Customization options are often restricted.
- Less Unique Designs: Since many websites use them, your site may look similar to others.
- Minimal Support: Free themes usually lack dedicated customer support.
Premium Themes
Premium themes are paid themes available from third-party marketplaces like ThemeForest, Elegant Themes, and TemplateMonster.
Advantages:
- Advanced Customization: More options to modify layouts, fonts, colors, and widgets.
- Better Performance: Optimized for speed, SEO, and mobile responsiveness.
- Regular Updates & Support: Comes with dedicated support and security updates.
Disadvantages:
- Costs Money: Prices range from $30 to $100+ per theme.
- Learning Curve: Some themes have complex settings and require technical knowledge.
- Potential Compatibility Issues: Might not work well with certain plugins or updates.
Which One Should You Choose?
If you are starting a small blog or personal website, a free theme should be enough. However, for business, eCommerce, or professional websites, a premium theme is a better investment.
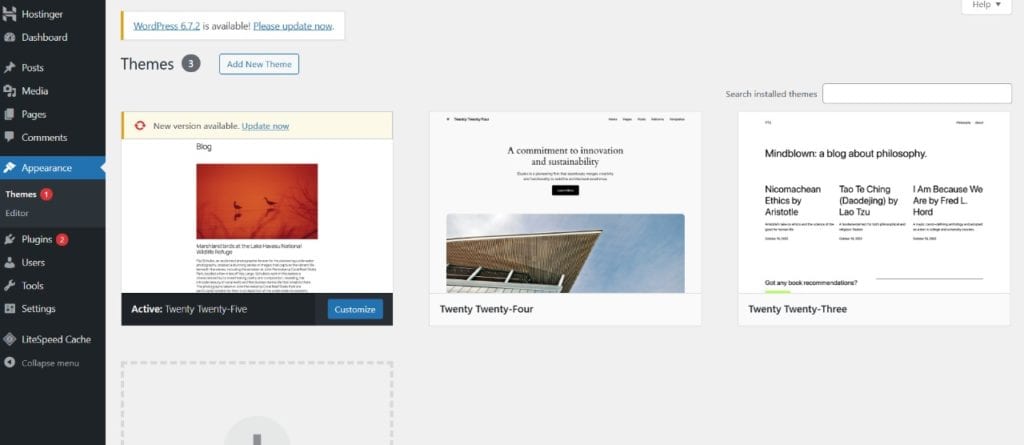
2. How to Choose the Right Theme?
With thousands of options available, choosing the right theme can be overwhelming. Here are some key factors to consider:
Purpose & Niche-Specific Design
If you are creating a blog, choose a theme with a clean layout for easy reading. For an eCommerce site, select a theme compatible with WooCommerce. A portfolio website should have a visually engaging design with gallery features.
Responsive & Mobile-Friendly Design
More than 50% of web traffic comes from mobile devices, so your theme must be mobile-friendly. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check if a theme adapts to different screen sizes.
SEO Optimization
A well-coded, SEO-friendly theme ensures faster loading times and better search rankings. Look for themes optimized for speed and structured data.
Customization Options
Some themes allow you to change colors, fonts, and layouts without coding. Check if the theme is compatible with page builders like Elementor, WPBakery, or Gutenberg for drag-and-drop customization.
Plugin Compatibility
Ensure the theme supports essential plugins such as:
- Yoast SEO (for SEO optimization)
- WooCommerce (for online stores)
- WPForms (for contact forms)
Regular Updates & Security
A good theme should receive frequent updates to stay compatible with the latest WordPress version and security patches.
Reviews & Ratings
Before installing a theme, check user reviews and ratings in the WordPress theme directory or third-party marketplaces.
3. Installing a Theme from the WordPress Repository
WordPress offers thousands of free themes in its official repository. You can install a theme directly from the WordPress dashboard.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing a Free Theme
1️⃣ Log in to Your WordPress Dashboard
- Navigate to yourwebsite.com/wp-admin.
2️⃣ Go to Appearance > Themes
- Click on “Appearance” in the left sidebar.
- Then, click on “Themes” > “Add New”.
3️⃣ Search for a Theme
- Use the search bar to find a theme by name or feature.
- You can filter themes by “Popular,” “Latest,” or “Featured.”
4️⃣ Preview & Install the Theme
- Hover over a theme and click “Preview” to see how it looks.
- Click “Install” to add it to your site.
5️⃣ Activate the Theme
- After installation, click “Activate” to make it live on your website.
✅ Your new theme is now active!
4. Uploading a Custom (Premium) Theme
If you purchase a premium theme or download a custom theme, you will need to upload it manually.
Step-by-Step Guide to Uploading a Custom Theme
1️⃣ Download the Theme ZIP File
- After purchasing a theme, download the .zip file from the theme provider (e.g., ThemeForest).
2️⃣ Log in to Your WordPress Dashboard
- Navigate to yourwebsite.com/wp-admin.
3️⃣ Go to Appearance > Themes
- Click on “Appearance” > “Themes” > “Add New”.
4️⃣ Upload the Theme
- Click “Upload Theme” and select the .zip file.
- Click “Install Now”.
5️⃣ Activate the Theme
- After installation, click “Activate” to apply the theme.
6️⃣ Customize the Theme Settings
- Go to Appearance > Customize to modify colors, fonts, and layouts.
Here is the short video how to install wordpress theme :
Customizing Your WordPress Website
Once you’ve installed a theme, the next step is to customize your WordPress website to match your brand identity and personal style. WordPress provides an easy-to-use Customizer that allows you to make real-time changes to your site’s appearance.
1. Using the WordPress Customizer
The WordPress Customizer is a built-in tool that lets you modify your website’s design without touching any code. You can access it directly from your WordPress dashboard.
How to Access the WordPress Customizer?
1️⃣ Log in to Your WordPress Dashboard
- Go to yourwebsite.com/wp-admin.
2️⃣ Navigate to the Customizer
- Click on Appearance > Customize.
3️⃣ Explore the Customization Options
- A live preview of your website will appear on the right.
- The left panel contains various customization settings.
👉 Changes made in the Customizer are visible in real time, but they will only be saved when you click the “Publish” button.
2. Adding a Logo, Site Title, and Tagline
A website’s logo, title, and tagline define its identity. These elements appear in the header and are crucial for branding.
Steps to Add a Logo, Site Title, and Tagline
1️⃣ Open the Customizer
- Go to Appearance > Customize > Site Identity.
2️⃣ Upload a Logo
- Click “Select Logo” and upload an image from your media library.
- WordPress allows cropping if needed.
3️⃣ Set the Site Title
- Enter your website’s name in the “Site Title” field.
- Example: “My Business Website”.
4️⃣ Add a Tagline
- Write a short description in the “Tagline” field.
- Example: “Your trusted source for digital solutions.”
- You can leave this blank if not needed.
5️⃣ Save Changes
- Click “Publish” to apply the updates.
👉 Tip: Choose a logo with a transparent background (PNG format) for a professional look.
3. Adjusting Colors and Typography
Changing Colors
Most WordPress themes allow you to customize the background color, text color, button color, and link color.
1️⃣ Go to the Customizer
- Navigate to Appearance > Customize > Colors.
2️⃣ Modify the Colors
- Change the background color using the color picker.
- Adjust text and link colors to match your branding.
3️⃣ Preview and Save
- Ensure the changes enhance readability.
- Click “Publish” to save your settings.
👉 Tip: Use a consistent color palette that aligns with your brand identity.
Changing Typography (Fonts & Sizes)
Typography plays a vital role in readability and aesthetics.
1️⃣ Go to the Customizer
- Navigate to Appearance > Customize > Typography (some themes may name it differently).
2️⃣ Modify the Fonts
- Select a Google Font or a theme-provided font.
- Adjust font sizes for headings, body text, and menus.
3️⃣ Preview and Save
- Check if the text remains readable across different devices.
- Click “Publish” to apply the changes.
👉 Tip: Avoid using too many different fonts—stick to one or two fonts for a clean and professional look.
4. Customizing the Homepage Layout
The homepage is the first impression visitors get of your website. WordPress allows you to customize the homepage layout based on your needs.
Setting a Static Homepage vs. Blog Page
By default, WordPress displays your latest posts on the homepage. However, you can set a static page as the homepage if you prefer a custom layout.
1️⃣ Open the Customizer
- Go to Appearance > Customize > Homepage Settings.
2️⃣ Choose the Homepage Display Option
- Select “Your latest posts” if you want a blog-style homepage.
- Select “A static page” to create a custom homepage.
3️⃣ Assign Pages
- If you select “A static page,” choose a page for:
- Homepage (e.g., “Home”)
- Blog Page (e.g., “Blog”)
4️⃣ Save Changes
- Click “Publish” to apply the new settings.
Installing and Using Plugins in WordPress
One of the biggest advantages of WordPress is its plugin system, which allows you to extend the functionality of your website without any coding knowledge. With over 60,000 free and paid plugins, you can add features like SEO optimization, security, performance improvements, contact forms, and more.
1. What Are WordPress Plugins?
A WordPress plugin is a piece of software that adds new features or enhances existing ones on your website.
Key Features of Plugins:
✔ Extend WordPress without coding.
✔ Available in free and premium versions.
✔ Cover various functions: SEO, security, backups, speed, eCommerce, etc.
✔ Can be installed and activated with just a few clicks.
Examples of What Plugins Can Do:
✔ Add a contact form (e.g., Contact Form 7)
✔ Improve SEO rankings (e.g., Rank Math, Yoast SEO)
✔ Speed up your website (e.g., WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache)
✔ Secure your website (e.g., Wordfence, Sucuri)
✔ Convert your site into an eCommerce store (e.g., WooCommerce)
👉 Think of plugins as “apps” for your WordPress site—each one adds a new feature!
- Here is Link below for installing plugins : https://learn.wordpress.org/lesson-plan/choosing-and-installing-plugins/
2. How to Install Plugins
Installing plugins is easy and can be done directly from the WordPress dashboard.
Installing Free Plugins from the WordPress Repository
1️⃣ Go to the WordPress Dashboard
- Navigate to Plugins > Add New.
2️⃣ Search for a Plugin
- Use the search bar to find a plugin (e.g., “SEO” or “Contact Form”).
3️⃣ Install the Plugin
- Click “Install Now” next to the plugin.
4️⃣ Activate the Plugin
- Click “Activate” to start using it.
👉 Example: Installing Yoast SEO for search engine optimization.
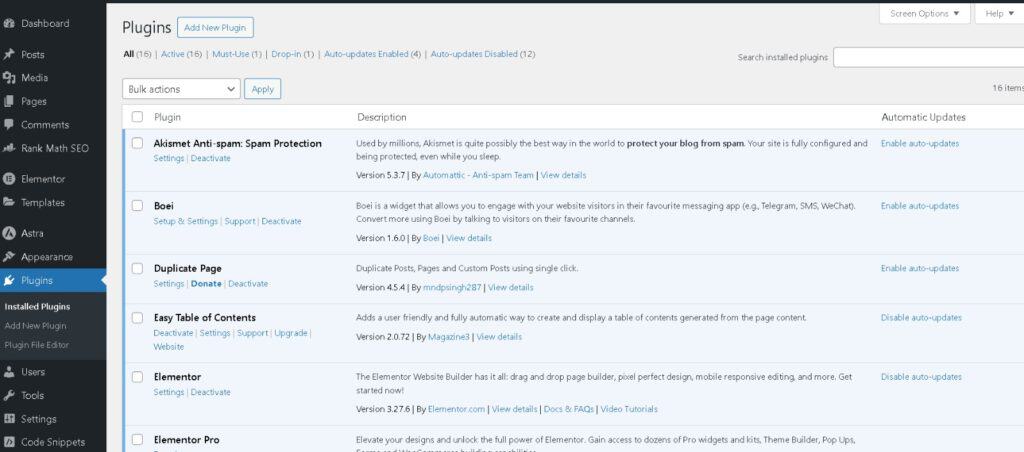
3. Deactivating and Deleting Plugins
Sometimes, you may need to deactivate or remove plugins to improve performance or security.
How to Deactivate a Plugin?
1️⃣ Go to Plugins > Installed Plugins.
2️⃣ Find the Plugin you want to deactivate.
3️⃣ Click “Deactivate”.
- The plugin will stop working, but settings will remain saved.
How to Delete a Plugin?
1️⃣ Go to Plugins > Installed Plugins.
2️⃣ Deactivate the Plugin First (if it’s active).
3️⃣ Click “Delete” under the plugin name.
4️⃣ Confirm “OK” when prompted.
👉 Tip: Regularly remove unused plugins to keep your website secure and fast.
Creating and Managing Content in WordPress
Content is important on any website, whether it’s a blog, business site, or eCommerce store. WordPress makes it easy to create, format, and organize content using Posts and Pages. In this section, we’ll cover:
1. Difference Between Posts and Pages
WordPress offers two main content types: Posts and Pages. Understanding the difference is crucial for structuring your website properly.
Pages
✔ Used for static, evergreen content that doesn’t change frequently.
✔ Examples: Home, About Us, Contact, Services, Privacy Policy
✔ Typically not listed by date and don’t have categories or tags.
✔ Organized in a hierarchical structure (e.g., a “Parent” page can have “Child” subpages).
👉 Best for: Permanent content like company information, landing pages, and legal pages.
Posts
✔ Used for blog articles, news updates, and time-sensitive content.
✔ Organized by categories and tags to make navigation easier.
✔ Displayed in reverse chronological order (latest first).
✔ Support comments (if enabled) for user interaction.
👉 Best for: Blogs, news, tutorials, and ongoing updates.
Here is the link below to know about pages and posts : https://wordpress.com/support/post-vs-page/
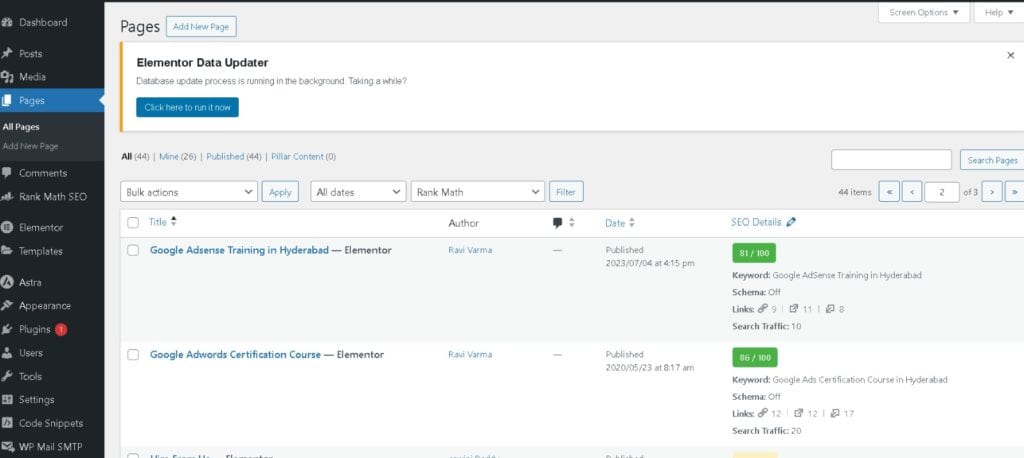
2. How to Create a New Page
Creating a new page in WordPress is simple. Follow these steps:
1️⃣ Go to the WordPress Dashboard
- Log in to your site (yourwebsite.com/wp-admin).
2️⃣ Navigate to Pages > Add New
- Click “Pages” in the left sidebar.
- Then, click “Add New”.
3️⃣ Enter a Title and Content
- In the Title field, type the page’s name (e.g., “About Us”).
- Add content using the WordPress Block Editor (Gutenberg).
4️⃣ Format the Page
- Use Headings (H1, H2, H3) for better readability.
- Add images, bullet points, and videos.
5️⃣ Publish the Page
- Click “Publish” to make it live.
👉 Tip: Pages do not appear in your blog feed. You can add them to your site’s navigation menu under Appearance > Menus.
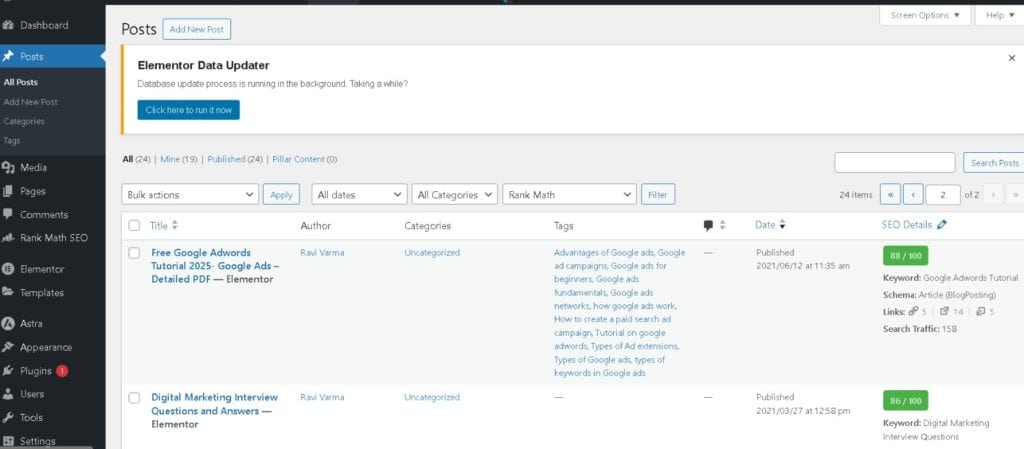
3. How to Write a Blog Post
Creating a blog post is similar to creating a page, but with added categorization options.
1️⃣ Go to the WordPress Dashboard
- Click on “Posts” > “Add New”.
2️⃣ Enter the Post Title
- The title should be clear, engaging, and include keywords for SEO.
- Example: “10 Essential SEO Tips for Beginners”.
3️⃣ Write the Content
- Use the WordPress Block Editor to add text, images, and videos.
- Structure content with headings (H2, H3) for readability.
4️⃣ Use Categories and Tags
- Assign Categories to group related posts (e.g., “SEO,” “Digital Marketing”).
- Add Tags to highlight specific topics (e.g., “SEO basics,” “Google ranking”).
5️⃣ Set a Featured Image
- Click “Set Featured Image” to choose a thumbnail for your post.
6️⃣ Preview and Publish
- Click “Preview” to check the post’s layout.
- Click “Publish” to make it live.
👉 Tip: Write engaging introductions and include a Call-to-Action (CTA) at the end of your posts.
Managing Menus and Navigation in WordPress
Navigation menus play a crucial role in improving user experience and site accessibility. A well-structured menu helps visitors easily navigate your website, find important pages, and explore content efficiently.
1. Creating and Editing Menus in WordPress
What Are WordPress Menus?
Menus in WordPress are customizable navigation bars that allow users to navigate different sections of a website. You can add pages, posts, categories, or custom links to a menu.
How to Create a Menu?
Follow these steps to create a new menu in WordPress:
1️⃣ Go to the WordPress Dashboard
- Navigate to Appearance > Menus.
2️⃣ Create a New Menu
- Click “Create a New Menu”.
- Enter a menu name (e.g., “Main Menu” or “Footer Menu”).
- Click “Create Menu”.
3️⃣ Choose the Menu Location
- WordPress themes provide different menu locations (e.g., Primary, Footer, Sidebar).
- Select where you want the menu to appear.
4️⃣ Save the Menu
- Click “Save Menu” to store your changes.
Now, your menu is ready! You can start adding items to it.
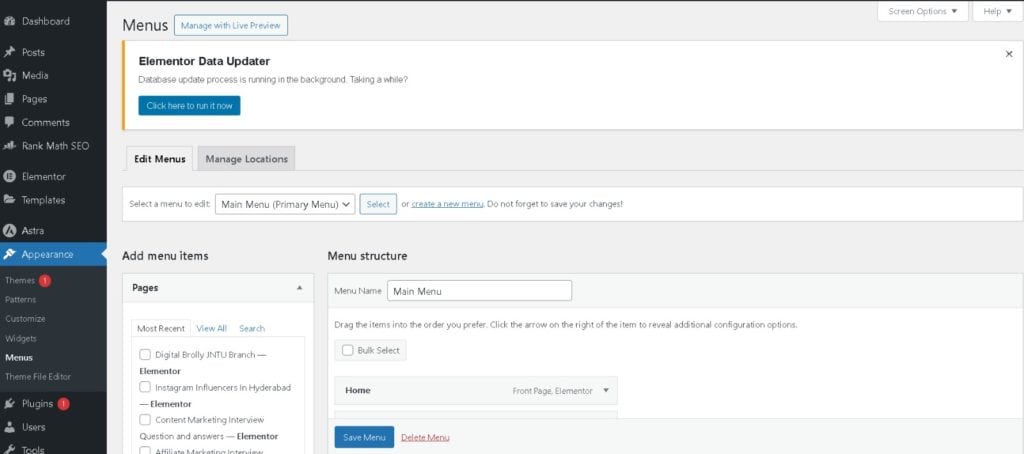
2. Adding Pages, Posts, and Custom Links to Menus
Once you’ve created a menu, you can add different items to it:
Adding Pages to the Menu
✔ Under “Add Menu Items”, click the “Pages” tab.
✔ Select the pages you want to add (e.g., Home, About, Contact).
✔ Click “Add to Menu”.
✔ Drag and drop the items to rearrange the order.
✔ Click “Save Menu”.
Adding Blog Posts to the Menu
✔ Click the “Posts” tab.
✔ Select the blog posts you want to add.
✔ Click “Add to Menu” and rearrange as needed.
✔ Click “Save Menu”.
Adding Custom Links to the Menu
You can add external links or links to specific sections of your website.
✔ Click the “Custom Links” tab.
✔ Enter the URL and the Link Text (e.g., “Visit Our Store”).
✔ Click “Add to Menu”.
✔ Click “Save Menu”.
3. Setting Up Dropdown Menus
A dropdown menu allows you to nest menu items under a parent category, improving navigation and organization.
How to Create a Dropdown Menu?
✔ Add multiple items to your menu.
✔ Drag a menu item slightly to the right under another menu item (this makes it a “submenu”).
✔ Repeat for other items as needed.
✔ Click “Save Menu”.
👉 Example: Services (Parent Item)
- SEO Training (Submenu)
- PPC Advertising (Submenu)
How to Remove a Menu Item?
✔ Click the dropdown arrow next to the menu item.
✔ Click “Remove”.
✔ Click “Save Menu”.
- Here is the link below to know more about menus: https://wordpress.com/support/menus/
WordPress Widgets and Sidebars: A Beginner’s Guide
Widgets and sidebars play an essential role in improving the functionality and design of a WordPress website.
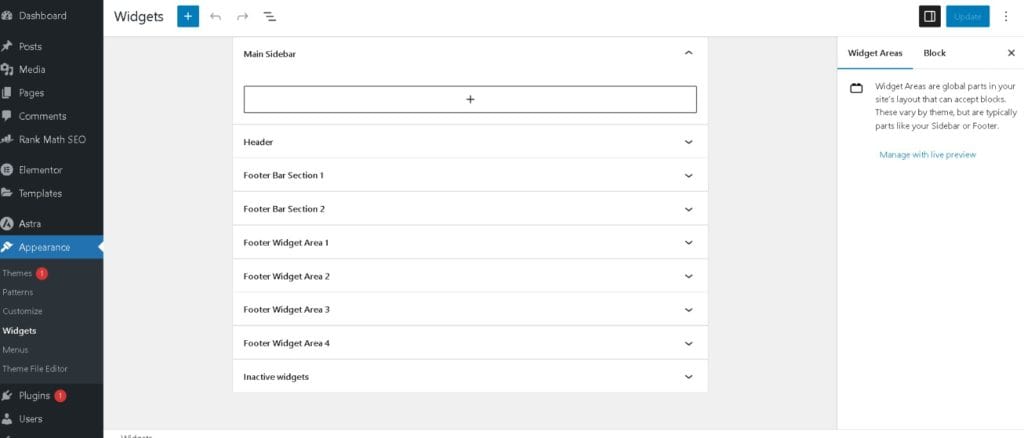
What Are WordPress Widgets?
Widgets are small content blocks that can be added to specific areas of a WordPress website, such as sidebars, footers, and headers. They help improve user experience by making the site more functional and engaging.
For example, you can use widgets to:
✔️ Add a search bar to help visitors find content quickly.
✔️ Show a list of recent posts to keep readers engaged.
✔️ Display a social media follow button to increase followers.
✔️ ️ Embed a contact form for easy communication.
What Are WordPress Sidebars?
A sidebar is a vertical section of a webpage (usually on the left or right side) where widgets are placed. However, some WordPress themes also allow widgets in footers, headers, or even within content areas.
Common Widget Placement Areas:
- Sidebar – Often used for navigation menus, recent posts, or ads.
- Footer – Good for social media links, contact details, or copyright information.
- Header – Useful for search bars and call-to-action buttons.
Setting Up User Roles and Permissions in WordPress
WordPress allows multiple users to collaborate on a website while maintaining different levels of access. This is managed through user roles and permissions, ensuring security and proper workflow.
1. Understanding WordPress User Roles
WordPress has a built-in user role management system that defines what each user can and cannot do.
Default WordPress User Roles
Role | Permissions |
Administrator | Full control over the website (can add/delete users, install plugins, change themes, edit content). |
Editor | Can publish, edit, and delete any content (posts and pages) but cannot change site settings. |
Author | Can publish, edit, and delete only their own posts. |
Contributor | Can write and submit posts for review but cannot publish them. |
Subscriber | Can only manage their own profile (suitable for membership sites). |
👉 Tip: Assign roles carefully to avoid security risks. For example, don’t give Administrator access to a casual blog writer.
2. Adding New Users to WordPress
If you run a blog, eCommerce store, or business website, you might need to add team members to manage content, SEO, or customer support.
How to Add a New User?
1️⃣ Go to the WordPress Dashboard
- Navigate to Users > Add New.
2️⃣ Enter User Details
- Username (Required)
- Email Address (Required)
- First Name & Last Name (Optional)
- Website (Optional)
3️⃣ Set a Password
- Click “Generate Password” or enter a custom password.
- You can check “Send User Notification” to email login details to the user.
4️⃣ Choose a User Role
- Select one of the roles (Administrator, Editor, Author, etc.) based on their responsibilities.
5️⃣ Click “Add New User”
✅ The new user will receive an email with login details!
3. Managing User Permissions
You can modify user roles and permissions anytime based on their needs.
How to Edit or Change User Roles?
✔ Go to Users > All Users.
✔ Find the user whose role you want to edit.
✔ Click “Edit” under their username.
✔ Scroll to the “Role” dropdown menu and select a new role.
✔ Click “Update User”.
✅ The user’s permissions will change immediately.
How to Remove a User?
✔ Go to Users > All Users.
✔ Hover over the user’s name and click “Delete”.
✔ If the user has published content, WordPress will ask:
- Reassign content to another user (recommended).
- Delete all content (not recommended unless necessary).
✔ Click “Confirm Deletion”.
👉 Tip: Regularly review user accounts and remove inactive or unnecessary users to enhance security.
Here is the short video for setting up user roles and permissions
Speed Optimization for WordPress
Website speed is a crucial factor that affects user experience, SEO rankings, and overall website performance. A slow-loading website can drive visitors away and negatively impact conversions. In this guide, we will cover why website speed is important, how to optimize images and caching, and how to use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for faster loading times.
1. Importance of Website Speed
Why Website Speed Matters
A fast website ensures a smooth user experience, better SEO rankings, and higher conversion rates. Here’s why speed optimization is essential:
✔ Better User Experience: Visitors expect a site to load in 2-3 seconds. A slow site increases bounce rates.
✔ Improved SEO Rankings: Google considers page speed as a ranking factor. Faster websites rank higher in search results.
✔ Higher Conversions: Studies show that a 1-second delay in loading time can reduce conversions by 7%. Faster pages lead to better sales and engagement.
✔ Better Mobile Performance: With mobile-first indexing, fast mobile loading speeds are essential for SEO and user experience.
How to Check Your Website Speed
Before optimizing, check your site’s speed using these tools:
✔ Google PageSpeed Insights (core web vitals) – Provides performance reports for mobile and desktop.
✔ GTmetrix – Analyzes loading time, page structure, and suggests improvements.
2. Optimizing Images and Caching
Optimizing Images for Faster Loading
Images are essential for a visually appealing website, but large image files can slow down your site. Optimizing images reduces their size without losing quality.
Best Practices for Image Optimization
✔ Use Proper Image Formats – Use JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics, and WebP for better compression.
✔ Compress Images – Reduce file size using tools like:
- Smush (WordPress plugin)
- Imagify (WordPress plugin)
✔ Resize Images Before Uploading – Uploading large images and resizing them in WordPress increases load time. Resize them before uploading using tools like Canva or Adobe Photoshop.
✔ Enable Lazy Loading – Lazy loading ensures images load only when they appear on the user’s screen, reducing initial page load time. Use plugins like: Lazy Load by WP Rocket
Caching for WordPress Speed Optimization
Caching improves website speed by storing static versions of your website instead of loading it from scratch every time a user visits.
Types of Caching:
- Browser Caching – Stores files in a visitor’s browser to reduce load time on return visits.
- Page Caching – Saves fully loaded pages as static files for faster delivery.
- Object Caching – Stores database queries to speed up dynamic content.
3. Using a CDN for Faster Loading
What is a CDN (Content Delivery Network)?
A CDN is a network of servers distributed worldwide. Instead of loading content from your main server, a CDN delivers cached website content from the nearest server to the user’s location, improving load time.
How a CDN Improves Speed
✔ Reduces Server Load – Less strain on your hosting server.
✔ Faster Page Load Times – Delivers content from a closer location.
✔ Better Global Performance – Great for international audiences.
✔ Enhanced Security – Many CDNs offer DDoS protection.
- Here is the link below to speed optimization : https://wordpress.com/support/site-speed/
Securing Your WordPress Website
Security is one of the most critical aspects of running a WordPress website. Hackers, malware, and brute-force attacks can compromise your site, leading to data loss, downtime, and even financial loss. Fortunately, WordPress offers multiple security measures to protect your website.
1. Common Security Threats in WordPress
Why WordPress Websites Get Hacked
WordPress powers over 40% of websites worldwide, making it a common target for hackers. Some of the biggest threats include:
How to Check Your Website Speed
✔ Brute Force Attacks – Automated bots try multiple password combinations to break into your website.
✔ Malware & Viruses – Malicious software can infect your site and steal data.
✔ SQL Injections – Hackers insert harmful SQL queries into your website’s database.
✔ Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) – Attackers inject harmful scripts to steal user data.
✔ DDoS Attacks – Hackers overload your website with traffic, causing it to crash.
✔ Plugin & Theme Vulnerabilities – Outdated or poorly coded plugins can create security loopholes.
How to Check If Your WordPress Site Is Hacked
✔ Your website suddenly becomes slow or unresponsive.
✔ You notice unauthorized admin users in your dashboard.
✔ Your homepage is replaced with a defaced page.
✔ Google flags your website as “This site may be hacked.”
If you suspect a hack, scan your website with Sucuri SiteCheck (sitecheck.sucuri.net) or Wordfence Security Scanner.
2. Installing Security Plugins to Protect WordPress
Security plugins help protect your website by adding firewalls, malware scanning, and login protection. Here are the best security plugins for WordPress:
Wordfence Security
- Scans for malware and suspicious activity.
- Blocks brute force login attempts.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs):
WAFs act as the first line of defense against malicious traffic by filtering and monitoring HTTP requests. They protect websites from threats like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and DDoS attacks, helping to mitigate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Advanced Malware Scanning and Removal:
Routine malware scans are essential, but advanced tools provide real-time threat detection. These tools identify known malware signatures and use heuristic analysis to detect suspicious patterns, ensuring faster response times to potential attacks.
WordPress Hardening Techniques:
For WordPress websites, hardening practices include disabling file editing from the dashboard, restricting access to core files, implementing two-factor authentication (2FA), and limiting login attempts. These steps minimize entry points for hackers and strengthen site security.
WordPress Hardening Techniques:
For WordPress websites, hardening practices include disabling file editing from the dashboard, restricting access to core files, implementing two-factor authentication (2FA), and limiting login attempts. These steps minimize entry points for hackers and strengthen site security.
Database Security Best Practices:
Protecting the database is crucial. This includes using strong, unique passwords, changing the default table prefix to prevent SQL injection attacks, and configuring proper user roles and permissions. Regular backups and encryption methods also ensure that sensitive data remains secure.
By implementing these advanced security measures, websites can move from being merely reactive to proactively defending against sophisticated cyber threats. Prioritizing security not only protects a site’s functionality but also builds credibility and trust among users — essential elements for long-term online success.
Backing Up Your WordPress Website
Backups are an essential part of website security and maintenance. If something goes wrong—such as a hack, a server crash, or accidental deletion—you can restore your website quickly without losing valuable data.
1. Why Backups Are Important
What Happens If You Don’t Have a Backup?
Without a backup, you risk permanently losing all website data in situations like:
- Hacking attacks – Hackers may inject malware or delete content.
- Server failure – Your hosting provider may experience downtime.
- Accidental deletion – You or a team member might delete important files.
- Incompatible updates – A WordPress update may break your site.
Benefits of Regular WordPress Backups
✔ Prevents Data Loss – Ensures your files and database are safe.
✔ Quick Recovery – Reduces website downtime after an issue.
✔ Security Against Attacks – Restores your site after hacking attempts.
✔ Peace of Mind – You can experiment with updates without fear.
2. How to Backup WordPress (Manual)
You can back up your WordPress website manually.
Manual Backup
Manual backups allow you to store files on your own system and provide full control.
Step 1: Backup Your WordPress Files
- Log into Your Hosting Account (cPanel, Plesk, or FTP).
- Open File Manager or connect via FTP (FileZilla).
- Locate the public_html folder (contains all your WordPress files).
- Download all files and save them to your computer.
Step 2: Backup Your WordPress Database
- Log in to phpMyAdmin via cPanel.
- Select your WordPress database from the left panel.
- Click Export > Choose SQL format > Click Go.
- Save the database file to your local storage.
Where to Store Manual Backups?
✔ Google Drive
✔ Dropbox
✔ External Hard Drive
✔ Cloud Storage
3. Restoring a Backup in WordPress
If your site crashes or gets hacked, restoring a backup is essential to bring it back online.
Method 1: Restore a Backup Manually
- Re-upload your website files to the public_html folder using FTP or File Manager.
- Open phpMyAdmin, select the database, and click Import.
- Upload the previously saved SQL database file.
Method 2: Restore a Backup Using UpdraftPlus
- Go to Settings > UpdraftPlus Backups.
- Click Restore and select the latest backup file.
- Choose what to restore (Database, Plugins, Themes, or Entire Site).
- Click Restore and wait for the process to complete.
Method 3: Restore from Hosting Provider
Many hosting providers (like Bluehost, SiteGround, and Kinsta) offer built-in backups.
- Log in to your hosting account.
- Find Backup Management under cPanel or Hosting Dashboard.
- Select the most recent backup and click Restore.
Here is the link below to know more about BackUp and Restore Your Website : https://wordpress.com/support/restore/
Troubleshooting Common WordPress Issues
WordPress is a platform, like any software, it can encounter issues. Some of the most common problems include the White Screen of Death (WSOD), plugin conflicts, 404 errors, and security breaches. Understanding how to troubleshoot these problems will save you time and help keep your website running smoothly.
Fixing the White Screen of Death (WSOD)
The White Screen of Death (WSOD) occurs when your website displays a blank white screen without any error message. This can be caused by plugin conflicts, theme issues, memory limit exhaustion, or corrupted files.
To fix this, start by increasing the PHP memory limit. You can do this by editing the wp-config.php file in your website’s root directory and adding the following line:
php
CopyEdit
define(‘WP_MEMORY_LIMIT’, ‘256M’);
If that doesn’t work, try disabling plugins via FTP. Rename the wp-content/plugins/ folder to plugins-disabled, which will deactivate all plugins. If your site loads properly afterward, reactivate the plugins one by one to identify the faulty one. Similarly, switching to a default WordPress theme like Twenty Twenty-Three can help determine if the issue is theme-related.
Resolving Plugin Conflicts
Plugin conflicts often occur when two or more plugins interfere with each other’s functionality. Common signs of plugin conflicts include a broken website, slow performance, or missing features.
To fix this, deactivate all plugins and then reactivate them one by one, checking your site after each activation. If the issue reappears, the last plugin activated is likely the cause. Look for an updated version of the plugin or find an alternative. Keeping plugins updated and using only reputable plugins can help prevent conflicts.
Dealing with 404 Errors and Broken Links
A 404 error occurs when a web page is missing or the URL structure is incorrect. This can frustrate visitors and harm your SEO ranking. The most common cause of 404 errors is a misconfigured permalink structure.
To fix this, go to Settings > Permalinks in the WordPress dashboard and click Save Changes to refresh the settings. If certain pages are still missing, you may need to set up 301 redirects using a plugin like Redirection or Rank Math SEO. Google Search Console can also help you identify and fix broken links.
Restoring a Hacked WordPress Website
If your WordPress site has been hacked, you need to act fast to prevent further damage. Some signs of a hacked site include unexpected redirects to spam websites, new unknown users in your admin panel, or your site being flagged by Google as insecure.
The first step is to scan your website for malware using security plugins like Wordfence or Sucuri. If the infection is detected, you may need to restore your site from a recent backup using a plugin like UpdraftPlus. Next, reset all admin, FTP, and database passwords, and update WordPress, themes, and plugins to their latest versions.
To prevent future attacks, install a security plugin, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), and use a web application firewall (WAF) to block malicious traffic. Removing unused plugins and themes can also reduce security risks.
- Here is the link below to know most common errors in wordpress Learn More : https://developer.wordpress.org/advanced-administration/wordpress/common-errors/
Want to learn Digital Marketing?
Join our Digital Marketing Course at Digital Brolly and get real-time experience. Learn from experts with live projects and interactive sessions.
WordPress Tutorial for Beginners - FAQ's
Yes, WordPress.org is free, but you need to pay for hosting and a domain name.
WordPress.org is self-hosted and gives full control, while WordPress.com is hosted with limited customization options.
You can Install WordPress via one-click installation from your hosting provider or manually upload files via FTP.
Look for a responsive, SEO-friendly, fast, and customizable theme. Popular options include Astra, GeneratePress, and OceanWP.
Plugins are add-ons that extend your website’s functionality, such as SEO optimization, security, and contact forms.
Use caching plugins, compress images, enable a CDN, minimize plugins, and choose a fast web host.
Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), install security plugins (Wordfence/Sucuri), and keep everything updated.
Use backup plugins like UpdraftPlus or manually back up files via FTP and database via phpMyAdmin.
Yes, using the WooCommerce plugin, you can set up an online store to sell products.
Install WPForms or Contact Form 7 to create a simple and user-friendly contact form.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) improves rankings on Google. Use Yoast SEO, create SEO-friendly content, and optimize images.
Install the MonsterInsights plugin or manually insert the Google Analytics tracking code in the header.
Yes, but some settings, layouts, and customizations may need adjustments after switching themes.
Most hosting providers offer free SSL certificates. You can also use the Really Simple SSL plugin to enforce HTTPS.
You can make money using Google AdSense, affiliate marketing, selling products, offering memberships, or sponsored posts.
